

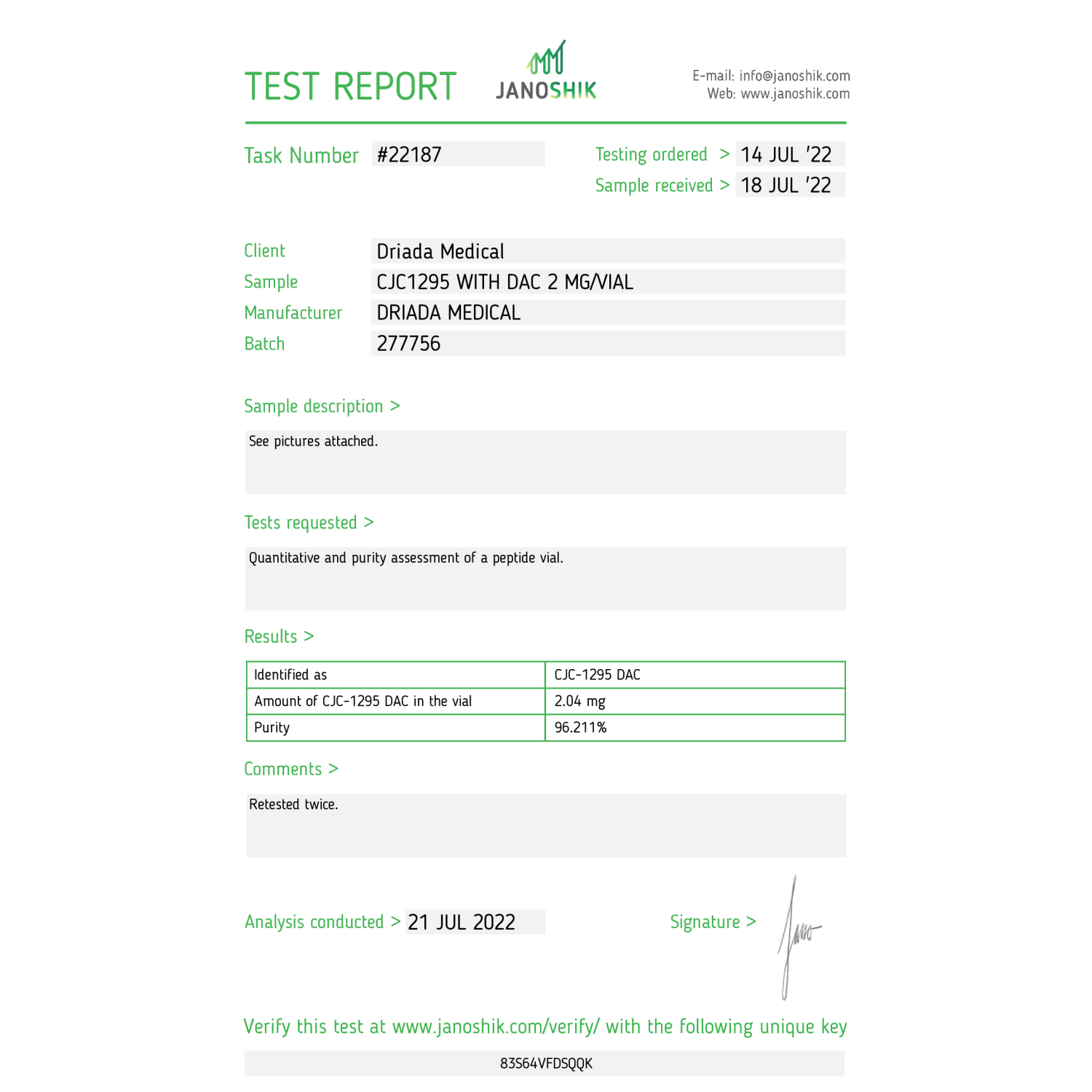



- Stock: In Stock
- Package: 2mg/vial+water
Description
CJC-1295 is a peptide hormone that consists of 30 amino acids. In the human body, it functions as an analog of somatoliberin (a natural stimulator of growth hormone secretion). It works on the nucleus of the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates the secretion of growth hormone. The substance binds to GHRH receptors, which belong to the group of G-protein-coupled receptors. The CJC-1295 version of DAC (Drug Affinity Complex) binds to plasma proteins (albumin), which leads to a significant increase in the duration of action, due to the addition of lysine bound to the non-peptide DAC molecule (the version without DAC lasts 30 min).
GHRH GROUP
The abbreviation GHRH stands for Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone or Somatoliberin. Somatoliberin growth hormone releasing hormone, also known as somatotropin-releasing factor (GRF, GHRF) or somatocrinin, is a releasing hormone for growth hormone. It is 44 amino acid peptide hormone produced in the hypothalamus.
Mechanism of action
Somatoliberin is released from the nerve endings of these arcuate neurons and is transported to the anterior pituitary gland, where it stimulates the secretion of growth hormone by stimulating special receptors. GHRH is released in pulsatile manner, stimulating a similar pulsatile release of growth hormone. In addition, somatoliberin also directly contributes to slow wave sleep.
The action of somatoliberin is opposite to the action of somatostatin (a hormone that inhibits growth hormone). Somatostatin is released from the neurosecretory nerve endings of periventricular somatostatin neurons and transported to the anterior pituitary gland, where it inhibits growth hormone secretion. Somatostatin and somatoliberin are secreted in turn, causing a largerly pulsatile secretion of growth hormone.
Petides of the GHRH group work only when the level of somatostatin in the blood is low, or the activity of this hormone is minimal. And this happens only at a time when the level of growth in the blood rises either after natural releases or after injections. It is possible, but rather difficult, to determine when endogenous growth hormone will be released into the blood and, accordingly, to adjust the injection of the GHRH peptide to it. Therefore, in practice, the following method is used: the GHRH group stimulantis injected after the GHRH group stimulant. Less oftenafter an injection of exogenous somatotropin.
GHRH peptides increase the level of endogenous growth hormone and this is followed by the positive effects inherent in growth hormone. This hormone plays a key role in regulating body composition. An important property of growth hormone is its powerful lipolytic effect. The administration of growth hormone to people with its deficiency reduces body fat mass and significantly increases lean body mass. Growth hormone enhances lipolysis directly by reducing the action of a number of lipogenic enzymes and indirectly by increasing the production of other lipolytic hormones such as catecholamines and glucagon, as well as by increasing the expression of adipocyte adrenoreceptors. In general, these effects lead to an increase in the utilization of body fat.
Growth hormone plays an important role as anabolic agent in human skeletal muscle and tendon connective tissue, which provide the matrix for the transmission of force from individual muscle fibers to bone. Thus, reinforced connective tissuewill give a stronger and more resistant muscle tendon structure. Because of this reason that growth hormone is used by athletes to treat muscle and tendon injuries. Similarly, high GH level improve bone strenght both directly and indirectly by increasing intestinal calcium absorption and serum vitamin D concentrations.
Purpose to use
One of the most highly regarded effects of growth hormone is its effect on muscle anabolism. Growth hormone induces uptake of glucose and amino acids and stimulates protein synthesis, possibly using energy derived from its lipolytic activity. Growth hormone entails an increase in the level of IGF-1 protein, which in turn also has a number of positive effects synergistic with growth hormone, such as a burning fat, increasing muscle mass and strenghtening bone and tendon structures. Reasons to consider the use of GHRH peptides may include increased fat loss, improved muscle gain, reduced choleserol and triglyceride levels and improved healing after injuries. Some of the substances of the GHRH group have successfully migrated to the category of pharmacological drugs, but most are still undergoing research or clinical trials.
Advantages
- No negative impact on blood sugar levels
- Forms a natural pulsating character of growth hormone peaks in the blood
Effects
- Sustained increase in groth hormone and IGF-q levels
- Reduce visceral adipose tissue
- Reducing total cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood
- Increased muscle mass
Side effects
- Short-term facial redness and pain at the injection site
- Arthralgia that occurs in different joints of the musculoskeletal system
- Myalgia (is a syndrome of pain in muscles, ligaments, tendons and fasciaconnective tissue membranes of muscles)
Predecessors of CJC1295
Tesamorelin, GRF (1-44)
Tesamorelin is one of the first growth hormone stimulants. A long time ago, reaserchers found that the last 15 amino acids of the somatoliberin chain are useless which is why sermorelin was created as a sequence of the first twentynine amino acids. But all 44 amino acids were left in the resamorelin chain, moreover, a trans-3-hexonoyl group was also added to them. This was done to prolong the period of effectiveness of the drug the period of its effective activity is no less than 4-5 hours. Tesamorelin is very actively used in medical practice like no other growth hormone secretion stimulator. Even despite the fact that today there are more effective drugs in this group. The effectiveness of the manuafacturer's recommended daily dose (2 mg, this is if the drug is used by itself) of tesamorelin is approximately equal to the effectiveness of three IU of synthetic growth hormone.
Sermorelin, GRF (1-29)
Sermorelin is one of the few peptides that have successfully passed stage of clinical trials and actively used in medical practice. The structure of sermorelin corresponds to a fragment of somatoliberin (amino acids 1-29, which is reflected in the second name of this drug GRF (1-29). The action is completely similar to somatoliberin. It is very short-lived, although the period of effective activity lasts up to two hours, and is not particularly powerful. But when combined with peptides of the GHRP group, it can significantly increase growth hormone levels.
Mod GRF (1-29)
In fact, it is sermorelin, but with a longer half-life. In 2005, reaserchers changed 4 amino acids in the GRF structurein the second, eighth, fifteenth and twenty-seventh positions. The resulting drug was called tetrasubstitued GRF (1-29), that is, GRF, in which 4 positions were substitued. In 2008, a researcher, known on the Internet under the nickname DatBtrue, proposed for the drug the name modified GRF (1-29) or Mod GRF (1-29) for shortunder this name he is known today. In our body, the path from the hypothalamus, where somatoliberin is synthesized, to thepituitary gland, where it should act is very short. The hormone does not encounter any obstacles along the way, so the half-life of GRF (1-29) is only 5 minutes. Based on this, it became necessary to create a drug with a longer half-life. One solution is Mod GRF (1-29), which has a half-life of 30 minutes.
CJC-1295 with DAC
On the basis of Mod GRF (1-29), a drug was created with an even longer half-life, which is already calculated in days. This drug was named CJC1295. This drug has the same amino acid sequence as Mod GRF (1-29), but also has the thirteenth amino acid, lysine, to which 3 maleimidopropionic acid is attached. This complex was named DAC (drug affinity complex). After that, Mod GRF (1-29) became known as CJC-1295 no DAC or simply CJC1295, and the real CJC-1295 was called CJC-1295 DAC. CJC-1295 is a very interesting drug that gives a good effect over a long period of time: in experiments it was used without interruption for up to six months or even more. Moreover: the emissions of one's own growth hormone are still of the same pulsating nature, that is, they are quite natural, just stronger.
How to use?
Dosage
1000-2000 mcg two times per week is the recommended dosage
Application scheme
Almost all drugs of the GHRH group have a very short half-lifeit is calculated in minutes. true, the period of effective activity is slightly higher, but, nevertheless, it does not exceed a couple of hours. Therefore, the frequency of injections should be at least 3-4 per day. The group includes one drug with a very long period of activity CJC 1295 DAC, injections of which can be carried out twice a week.
Combination with other drugs
GHRH drugs are not usually used alone, but are most often used in combination with a GHRP class peptide such as GHRP-2, GHRP-6, hexarelin or ipamorelin. Examples of use are 100 mcg CJC1295 taken concomitantly with 100 mcg GHRP-6 or ipamorelin. This combination is synergistic. GHRP stimulates the GH release impulse and GHRP amplifies it. Dosage when combined with GHRP should be approximately 100 micrograms. The dosage of CJC 1295 DAC should be 1000 mcg (1 mg) twice a week.
How to prepare a solution
In order to prepare a solution for injection, you take a syringe already containing a diluent and inject it into a vial containing a lyophilized powder. Tilt the vial so that the needle touches the vial wall. Avoiding injecting the diluent directly into the lyophilized powder. The solvent should slowly flow down the wall of the bottly (do not fill everything at once and take your time). Once all the diluent has been added to the paprtide vial, mix gently (but do not agitate or shake the vial) until the lyophilized powder has dissolved and you are left with a clear liquid. Now the drug is ready for use.
Never mix one peptide with another in the same syringe. This creates risks that fragile peptide molecules will be destroyed.
Application
- The injection can be subcutaneous, intramuscular, depending on personal preference.
Storage
- The resulting solution can be stored for approximately 21 days in a refrigerator at a temperature of 2-8C. The storage time increases if the solution was prepared using bacteriostatic water.


