- Stock: In Stock
- Package: 600 mg/vial + water х 10 vials
This offer ends in:
Recommended with this product
After a good stimulant, you need a good rest!
View moreIt's the B-group vitamins that are responsible for
View moreThe oral version of L-carnitine is excellent
View more
- Composition: glutathione 600 mg.
- Category: peptide, antioxidant.
- Purpose: muscle protection and recovery, improved endurance, detox, liver support.
- Form: 10 vials with 600 mg lyophilized powder + 10 ampoules with 4 ml of bacteriostatic water each.
- Administration: intravenous or intramuscular injections.
What is TAD-600 (Glutathione)?
TAD-600 is an injectable form of Glutathione, a powerful antioxidant naturally produced in the body. However, levels of Glutathione tend to drop during intense training, stress, or when using PEDs. Supplemental Glutathione helps fill that gap, offering protection for the muscles, liver, and overall cellular recovery.
Because it bypasses the digestive tract, the injectable form provides fast and efficient action. Once in the bloodstream, Glutathione goes to work supporting liver detox, reducing inflammation, and maintaining immune and skin health.
Main effects of TAD-600
- Reduces muscle inflammation and cellular damage after workouts.
- Speeds up recovery between training sessions.
- Helps protect the liver when using PEDs.
- Improves overall well-being and energy levels during heavy training.
- Evens out skin tone and supports skin quality.
- Strengthens antioxidant defense during stress or high-intensity training.
How to take TAD-600?
TAD-600 comes in vials containing 600 mg of Glutathione lyophilized powder and ampules with 4 mL bacteriostatic water. Before use, the powder must be reconstituted with the included bacteriostatic water. If you're new to peptide reconstitution or injection techniques, please read our guide HERE.
Most common protocols
600 mg (1 vial) 1 to 3 times weekly, depending on your goal:
- Once weekly for general wellness and maintenance.
- 2–3 times weekly if you're on a PED cycle or training under heavy physical stress.
What to keep in mind?
For those who are considering buying Glutathione online, it’s better to keep in mind:
- Do not use if allergic to Glutathione.
- Do not mix with other substances in the same syringe.
- Once reconstituted, store in the refrigerator and use within 24 hours.
- Avoid during active infections or fever.
Possible side effects
- Headache.
- Light dizziness or nausea.
- Mild irritation at the injection site (redness, itching).
- Rare allergic reactions.
How to store?
- Keep refrigerated at 2–8°C (36–46°F).
- Do not freeze.
- Protect from light and moisture.
- Avoid repeated temperature shifts.
- Use immediately after reconstitution.
How does TAD-600 work?
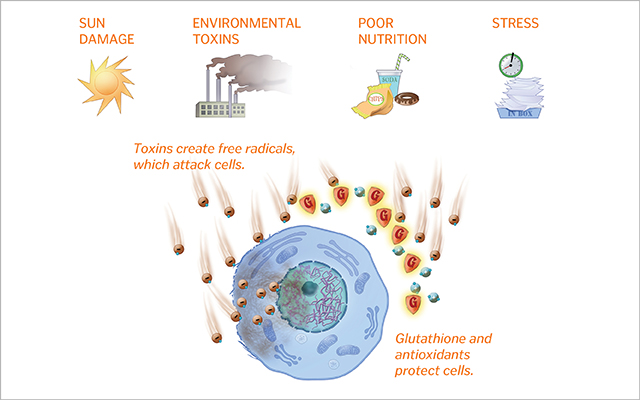
Neutralizing free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules formed during intense exercise, PED use, toxin exposure, or even just from breathing. Left unchecked, they damage cells, accelerate aging, and trigger inflammation. Glutathione helps neutralize these radicals by converting them into harmless compounds, protecting muscle and liver cells in the process.
Supporting detox pathways. Glutathione plays a central role in the body’s natural detox process. When the liver processes harmful substances, including medications and steroid metabolites, it relies on Glutathione to bind them and help flush them out through bile or urine. This reduces toxic load and supports liver function — especially important for athletes using PEDs or those under pharmaceutical stress.
Immunity and recovery. Glutathione helps the immune system function smoothly by activating key immune cells and reducing inflammation. When Glutathione levels drop (from training, PED use, or stress), the immune system may weaken, making recovery slower and the body more prone to illness.
Keeping glutathione levels high reduces this background inflammation and speeds up tissue repair. Athletes often report fewer illnesses and faster bounce-back during high-intensity periods. That’s why a lot of athletes go for injectable Glutathione, even if the price isn’t always low — the way it helps during tough training makes it worth it.
Skin pigmentation and tone. Glutathione slows down the activity of tyrosinase, an enzyme involved in melanin production. This is why many users report brighter and more even skin tone over time, especially with consistent use.
FAQ
What is TAD-600 mg used for?
TAD-600 is used to support the liver and speed up recovery after tough workouts or PED use. Many athletes take it to stay on track and feel better during intense training. Injectable Glutathione in TAD-600 has become a favorite among athletes, whether it’s on sale or not.
How to take TAD-600?
Mix the powder with the water from the ampoule. Inject slowly into a muscle or vein. Use one vial 1–3 times per week, depending on your goals.
What to avoid when taking Glutathione?
Don’t mix it with other drugs in the same syringe. Avoid if you’re sick or allergic to it. Smoking, alcohol, and junk food reduce its benefits.
Is it OK to take Glutathione every day?
You can, but it’s usually not needed. Most people get good results with 2–3 shots a week.








