






- Stock: In Stock
- Package: 2mg/vial+water
Recommended with this product
Regeneration, muscle growth, and fat burning-
View moreNeed ultimate regeneration?
View moreNandrolone cycles with peptides and
View more- Composition: TB500 (Thymosin Beta-4 Acetate fragment) 2 mg.
- Category: peptide.
- Purpose: tissue repair and healing support.
- Form: vial with 2 mg of lyophilized powder + 1 ml ampoule of injection water for reconstitution.
- Administration: subcutaneous injections.
What is TB500?
This is a synthetic peptide based on the natural protein thymosin beta-4, which plays a key role in the repair and healing process in all body tissues. TB-500 was developed for medical purposes to accelerate the healing of wounds and internal injuries, support recovery after surgery, and treat ligament, muscle, and tendon injuries. The peptide is also popular among athletes seeking effective and rapid recovery after intense training or injuries, as well as to increase tissue resistance to stress.
Main effects
🩹 Accelerated healing of wounds and injuries.
🦵 Recovery of muscles, ligaments, and tendons after heavy loads or injuries.
📉 Reduced inflammation.
🤸♀️ Improved tissue mobility and elasticity.
🌱 Stimulation of new capillary growth, which improves tissue nutrition.
🛡️ Strengthening the immune response.
🧖♀️ Accelerated healing of skin and mucous membranes.
💆♂️ Hair growth.
How to use TB500?
If you buy TB500 online for the first time, be sure to read the instructions for use. Medicine comes in a vial containing 2 mg of lyophilized powder. It must be reconstituted using the provided 1ml injection water before use.
Protocol example
| Phase | Dosage | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Phase | 2.0–2.5 mg every other day | 3–4 injections per week | 2–4 weeks |
| Standard Loading | 4–8 mg per week, split into 2–3 doses | 2–3 times per week (e.g. Mon/Thu/Sat) | 4 weeks |
| Maintenance Phase | 2–6 mg per month | 1 injection every 7–14 days | 4–8 weeks (or longer) |
Typical total cycle length: 6 to 12 weeks, depending on individual response, injury severity, and reassessment.
The dosage may be adjusted individually depending on:
- Severity of injury.
- Body weight.
- Body response.
| Popular combinations with TB-500 | Purpose |
|---|---|
| TB-500 + HGH | Strong synergy for soft tissue and muscle regeneration. |
| TB-500 + GHRP-2 / GHRP-6 | Boosts natural growth hormone release and speeds up recovery. |
| TB-500 + BPC-157 | Especially useful for tendon injuries and bone fractures. |
| TB-500 + HGH + BPC-157 | Maximized regenerative effect. |
| TB-500 + CJC-1295 / Ipamorelin | Supports GH release with extended activity via GHRH. |
Precautions
- Avoid use if you have active cancer or tumor history.
- Monitor for allergic reactions or unusual side effects.
- Not intended for continuous, year-round use without breaks.
- Buy TB500 peptide only from verified and trusted resellers.
Possible Side Effects
- Mild injection site irritation (redness, swelling, itching).
- Temporary fatigue or drowsiness.
- Headache.
- Nausea.
- Light dizziness.
- Hormonal imbalance (with prolonged or high-dose use).
- Water retention (rare).
- Tingling or numbness (very rare).
- Allergic reaction (rash, itching, swelling — discontinue use if occurs).
How to store?
- Before reconstitution (in powder form) for long-term storage, store in a cool place away from direct sunlight, best before, the expiration date is indicated on the product.
- After dilution, store in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2–6 degrees, avoid freezing and direct sunlight. The diluted peptide can be stored for about a month.
How does TB500 work?
Mobilizing repair cells via actin regulation
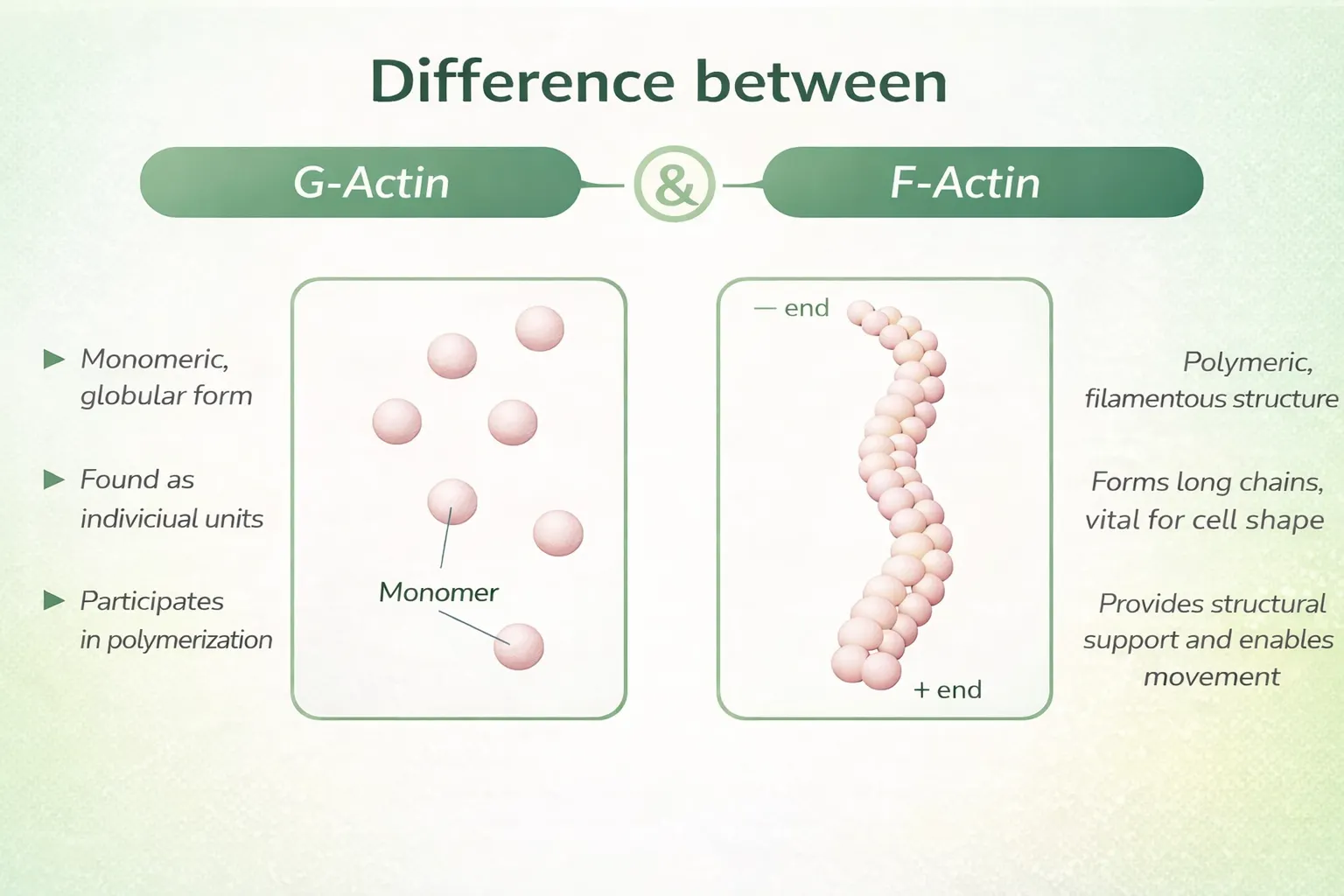
TB-500 binds to G-actin (globular actin), a protein found inside cells. By preventing it from turning into F-actin (filamentous actin), TB-500 helps regulate cell movement.
When a cell wants to move to the site of damage, it needs to flexibly and quickly change shape — for this it is important that there is enough free G-actin, and not just F-actin filaments.
- G-actin (globular actin) is a monomeric (single) form of actin that can quickly move to sites of damage/growth and is used for tissue construction.
- F-actin (filamentous actin) is assembled chains of G-actin that form structural fibers, like a skeleton within the cell.
TB-500 “binds” G-actin and prevents it from prematurely turning into F-actin. Thanks to this:
- cells migrate faster to damaged tissues;
- healing improves;
- the formation of scar tissue is reduced (less fibrosis);
- fabrics retain elasticity.
Stimulating angiogenesis (new blood vessels)
One of the most powerful effects of TB-500 is its ability to promote angiogenesis — the formation of new capillaries. This increases blood flow to damaged areas, improving oxygen and nutrient delivery, which speeds up healing and tissue repair.
TB-500 supports this process by mobilizing endothelial cells (the ones that form blood vessels), activating growth factors like VEGF, and reducing inflammation that might otherwise block capillary growth. As a result, new blood vessels form more easily, helping tissues recover faster and more efficiently.
The cardiovascular system
Scientists suggest that the healing properties of Thymosin Beta 4 can be used to regenerate human heart muscle damaged by a heart attack or other heart disease. Rodent studies have shown that the administration of Thymosin beta 4 stimulates the formation of new myocardial cells from inactive precursor cells present in the lining of the heart. Moreover, in damaged myocardium Thymosin Beta 4 has been found to promote angiogenesis and due to its anti-fibrotic effect, has a positive effect on myocardial cell remodeling.
It is known that the peptide promotes the migration, survival and recovery of heart cells, which was demonstrated in cell culture of embryonic and postnatal cardiomyocytes — cell survival was improved. Also, in in vivo experiments after coronary artery ligation in mice, treatment with Thymosin Beta 4 resulted in increased survival of early myocytes and improved cardiac function. Thymosin Beta 4 facilitates epicardial neovascularization in both injured and healthy adult mammalian hearts, which has been shown in an in vivo mouse model. Thymosil Beta 4 significantly improved long-term neurological recovery in a rat model of stroke.
Anti-inflammatory action
TB-500 helps regulate the immune response by reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhancing anti-inflammatory signaling. This is particularly useful in:
-
Chronic inflammation (like tendonitis).
-
Ligament strain.
-
Post-surgery recovery.
This effect also supports faster healing and less discomfort during recovery.
Eyesight
TB-500 can be used in ophthalmology. It is used in the treatment of dry eye syndrome and neurotrophic keratopathy. Animal studies have shown that it promotes rapid and complete healing of damaged corneas. It is worth noting that research in this area was carried out not only on animals, but also on humans. Patients with moderate to severe dry eye symptoms who received TB-500 eye drops reported significant and sustained improvement. In most people, the symptoms of the disease did not return after the end of treatment.
Hair growth
Scientists conducted a series of animal model studies to see how TB-500 affects hair growth. After analyzing the results, they come to a conclusion that this peptide can promote the development of stem cells in hair follicles, as well as promote their differentiation and migration. It is believed that this action accelerates hair growth.
FAQ
What is the difference between TB-500 and BPC-157 and can they be combined?
TB-500 works systemically, improving blood flow and accelerating healing of muscles, tendons and skin, while BPC-157 works more locally and is effective for inflammation and injuries of the ligaments or gastrointestinal tract. When paired, they provide a powerful synergistic effect and are often used together for accelerated recovery. You can buy TB500 and BPC-157 at the best prices in our online store.
Can TB-500 be used for preventive purposes — before injury?
Yes, TB-500 can be used preventively. Many athletes use it in low maintenance doses to support tissue flexibility, improve circulation, and reduce the risk of injury under heavy physical stress.
Can TB-500 be used locally by injecting into an injured area?
TB-500 can be injected near the injured area, but it’s not required. The peptide distributes systemically after injection, so even subcutaneous administration away from the injury still allows it to reach damaged tissues effectively.
Where can I find TB500 peptides for sale?
You can always purchase peptides at the best prices in our online store.








