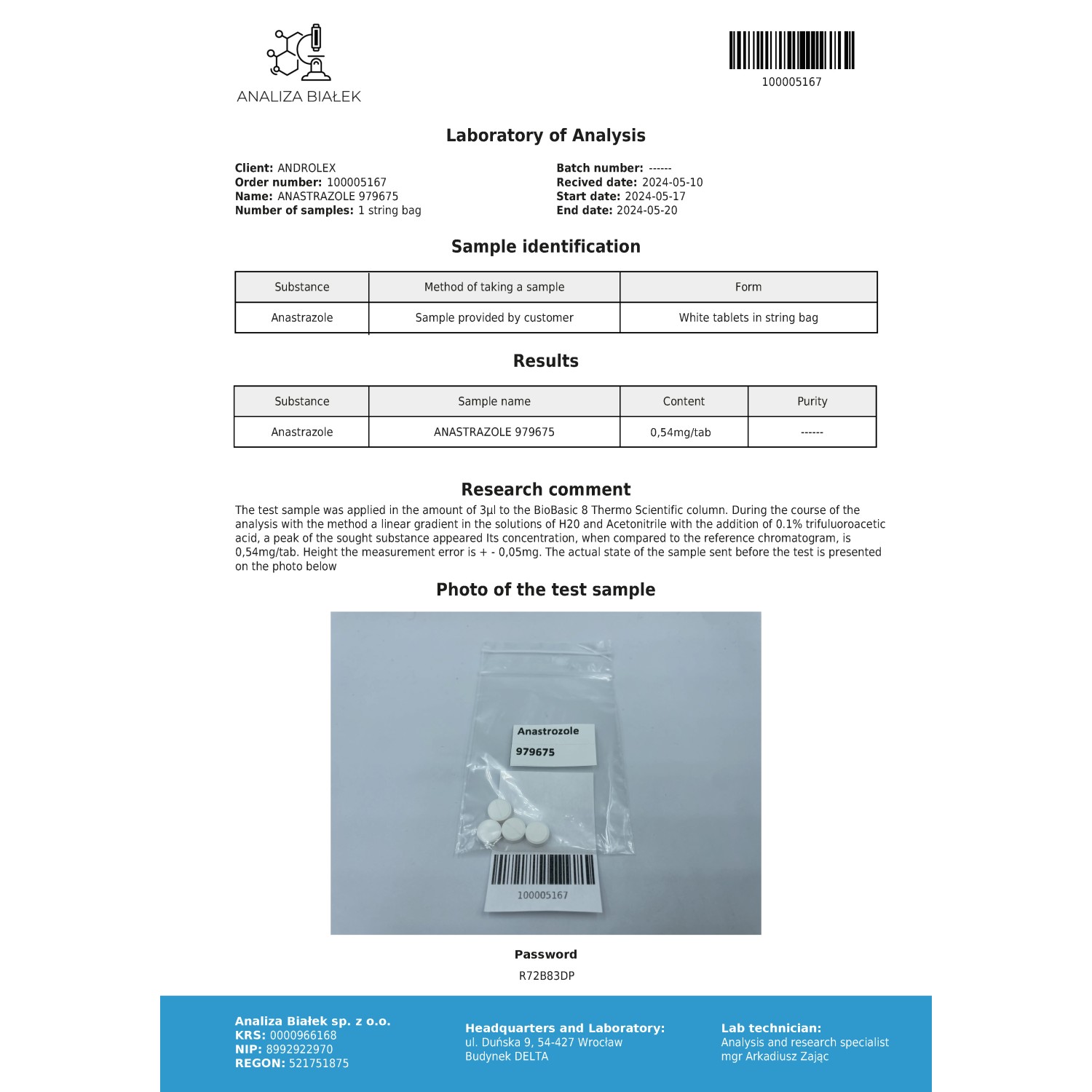


- Stock: In Stock
- Package: 0.5 MG/TAB
What is anastrozole?
Anastrozole is a drug that blocks the conversion of testosterone to estrogen. It was originally developed to treat breast cancer in women, but was later used in men as well, primarily to control estrogen levels during testosterone therapy or when aromatization is excessive.
Excess estrogen in men can cause gynecomastia, fluid retention, and decreased testosterone production. Anastrozole helps maintain a balance between androgens and estrogens, supporting hormonal balance.
Main effects of anastrozole
🧬 Reduces blood estradiol levels.
💪 Prevents gynecomastia and other estrogen-dependent effects.
⚖️ Maintains a normal testosterone-to-estrogen ratio.
💧 Reduces fluid retention and edema.
🔁 Potentially increases endogenous androgen levels through stimulation of LH and FSH.
How to take anastrozole?
When and how to start
The intake of anastrozole usually begins 1–2 weeks after the start of the androgen course, when testosterone levels and aromatase activity begin to rise.
If a short testosterone ester (for example, propionate) or oral compounds with strong aromatization (such as methandrostenolone) are used, anastrozole can be started earlier — after 5–7 days from the beginning of the cycle.
Before starting, it is advisable to perform blood tests for estradiol and testosterone to confirm an elevated estradiol level.
Approximate starting dosages
- 0.5 mg every other day — standard preventive approach for most androgen cycles.
- 0.5 mg twice per week — for moderate aromatization or during testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
- 1 mg every other day — only if blood tests show significantly elevated estradiol (>40 pg/mL).
The exact dosage and frequency should always be based on lab results, as sensitivity to aromatase inhibition varies among individuals.
How long to take
Anastrozole is taken until the end of the androgen course.
After the course is finished, its use may continue for another 2–4 weeks if tests show an elevated estradiol level.
Once hormone balance is restored, the drug is discontinued.
Compatibility
Anastrozole can be combined with:
- testosterone preparations (enanthate, cypionate, sustanon, etc.);
- human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG);
- post-cycle therapy agents (clomiphene, tamoxifen), but only under medical supervision.
It is not recommended to combine anastrozole with other aromatase inhibitors (letrozole, exemestane) or to use it preventively without medical indication — this may cause estrogen deficiency.
Precautions
- Intake should be carried out only after hormone testing.
- Not recommended to use without clear medical indication.
- Excessive suppression of estrogens may cause joint pain, mood decline, and reduced bone density.
- When combined with other hormonal agents, laboratory monitoring is necessary.
- The drug is contraindicated for premenopausal women.
Side effects
- Joint pain or stiffness.
- Increased cholesterol levels.
- Decreased libido and fatigue.
- Mood swings, irritability.
- Long-term use may lead to reduced bone density.
Storage
- Store in a dry, dark place at temperatures up to 25 °C.
- Keep away from moisture and out of reach of children.
How does anastrozole work?
Anastrozole blocks the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen (estradiol). When this process is inhibited, estrogen levels decrease, while testosterone levels relatively increase.
For men, this means a lower risk of gynecomastia, water retention, and hormonal imbalance. For women with hormone-dependent tumors, it reduces tumor stimulation by estrogens.
The drug’s half-life is approximately 40–50 hours, so it is taken no more than once daily or every other day, depending on the physician’s recommendation.


