
WHAT IS SEMAGLUTIDE?
Semaglutide is a safe, FDA approved medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists. Semaglutide has gained popularity in recent years as a treatment for type 2 diabetes and for weight loss in individuals who are overweight or have obesity and certain medical conditions. Semaglutide works by stimulating the release of insulin and suppressing the release of glucagon, which helps lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. In addition to its use in diabetes, Semaglutide has also been approved for use as a weight loss medication.
FDA APPROVED DRUG
Semaglutide was recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a weight loss medication. It works by reducing appetite and increasing feelings of fullness, leading to a reduction in food intake and subsequent weight loss.
BENEFITS OF USING SEMAGLUTIDE
Semaglutide, when used as a weight loss medication, can have several benefits, including:
- Significant weight loss: Clinical trials [1] have shown that semaglutide can lead to significant weight loss, with participants losing an average of 15% of their body weight over 68 weeks.
- Improved health outcomes: Losing weight can improve several health outcomes, including reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, lowering blood pressure, and improving cholesterol levels.
- Increased satiety: Semaglutide works by increasing feelings of fullness and reducing appetite, which can help reduce food intake and aid in weight loss.
- Convenience: Semaglutide is administered by injection once a week, making it a convenient treatment option for people who struggle to stick to a daily medication regimen.
HOW IT WORKS?
Semaglutide reduces total body weight and adipose tissue mass by reducing energy intake. This mechanism involves a general decrease in appetite, including an increase in satiety signals and a decrease in hunger signals, as well as improved control of food intake and a decrease in food cravings. Insulin resistance is also reduced, possibly due to weight loss. In addition, Semaglutide reduces the preference for high-fat meals. In animal studies, Semaglutide has been shown to be taken up by specific areas of the brain and increase key satiety signals and attenuate key hunger signals. By acting on isolated areas of brain tissue, Semaglutide activates neurons associated with satiety and suppresses neurons associated with hunger.
POSITIVE IMPACT ON HEALTH
In clinical studies, semaglutide had a positive effect on plasma lipids, lowered systolic blood pressure and reduced inflammation. In animal studies, Semaglutide inhibits the development of atherosclerosis by preventing further development of aortic plaques and reducing inflammation in the plaques. Compared with placebo[2], Semaglutide reduced caloric intake by 35% during three daily meals. Compared with placebo[3], Semaglutide reduced fasting triglycerides and VLDL cholesterol by 12% and 21%, respectively. Postprandial increases in triglycerides and VLDL cholesterol in response to a high-fat meal were reduced by more than 40%. Semaglutide reduced glucose levels after the first dose.
SAFETY
That being said, semaglutide has been extensively studied in clinical trials for weight loss and has been found to be generally well-tolerated. Semaglutide, like any medication, can have potential risks and side effects. Some common side effects of Semaglutide include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, constipation, and abdominal pain. These side effects are generally mild and tend to improve over time.
WHY DRIADA?
Semaglutide is an extremely popular drug that is sold in official pharmacies under the trade name Oz-pic. We also provide you with the same product under our brand that you can purchase at an affordable price and without the need to get a prescription from a doctor.
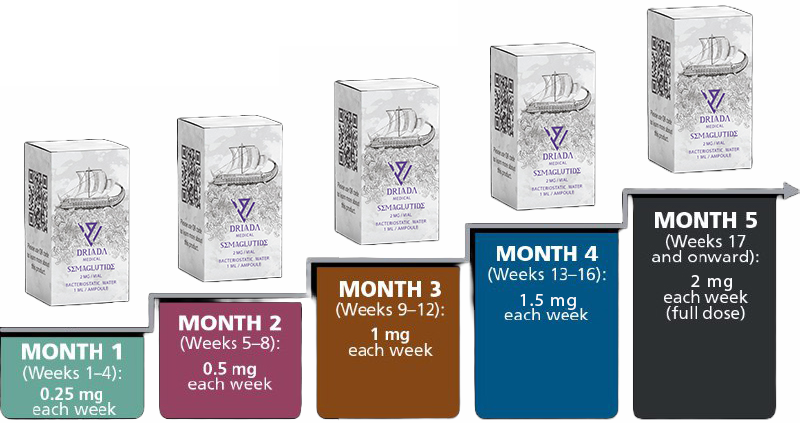
HOW TO USE?
- The recommended dose of semaglutide for weight loss is 2.4 mg once a week.
- For weight loss, the starting dosage of semaglutide is 0.25 mg once a week for four weeks. This will help give your body a chance to get used to the medicine.
- The second month you increase the dosage to 0.5 mg. The third month is up to 1 mg, the fourth month is about 1.7 mg and on the fifth month you go out at 2.4 mg per week.
- In general, starting at a lower dose and gradually increasing the dose over time may be recommended to minimize the risk of side effects. However, the appropriate dose of Semaglutide for weight loss will depend on a variety of factors, including your overall health, medical history, and other medications you may be taking.
Semaglutide for weight loss is available as a subcutaneous injection (injected under the skin) and is self-administered by the patient once a week.
COMBINATION WITH OTHER DRUGS FOR FAT BURNING
In order for you to get the maximum result, you can use this drug together with other drugs that help burn fat. A good combination may be the combined use of Semaglutide with Yohimbine or Clenbuterol, as well as with thyroid hormones. If you want to speed up the fat burning process as much as possible, then in addition to this, you can use growth hormone or HGH Fragment. All these combinations are suitable for both men and women.
HOW TO ACHIVE THE BEST RESULTS?
To achieve the best results with Semaglutide, it is important to use the medication as directed by a healthcare professional and to follow a healthy diet and exercise program. This may include reducing calorie intake, increasing physical activity, and making lifestyle changes that support weight loss and overall health.
Below we will give a possible version of the scheme for men and for women who want to improve their shape by the summer, burn fat and increase muscle mass. These dosages are suitable for beginners. by slightly increasing the dosages, more advanced athletes will also be able to use this scheme.
[1] Randomized Controlled Trial N Engl J Med
- 2021 Mar 18;384(11):989-1002. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183. Epub 2021 Feb 10.
- Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
- John P H Wilding 1, Rachel L Batterham 1, Salvatore Calanna 1, Melanie Davies 1, Luc F Van Gaal 1, Ildiko Lingvay 1, Barbara M McGowan 1, Julio Rosenstock 1, Marie T D Tran 1, Thomas A Wadden 1, Sean Wharton 1, Koutaro Yokote 1, Niels Zeuthen 1, Robert F Kushner 1; STEP 1 Study Group
- Collaborators, Affiliations expand
- PMID: 33567185 DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33567185
[2] Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Sep; 19(9): 1242–1251
- Published online 2017 May 5. doi: 10.1111/dom.12932
- PMCID: PMC5573908
- PMID: 28266779
- Effects of once-weekly semaglutide on appetite, energy intake, control of eating, food preference and body weight in subjects with obesity
- John Blundell, PhD,corresponding author 1 Graham Finlayson, PhD, 1 Mads Axelsen, MD, 2 Anne Flint, PhD, 2 Catherine Gibbons, PhD, 1 Trine Kvist, PhD, 2 and Julie B. Hjerpsted, PhD 2
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5573908
[3] Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Mar; 20(3): 610–619.
- Published online 2017 Oct 27. doi: 10.1111/dom.13120
- PMCID: PMC5836914
- PMID: 28941314
- Semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays first‐hour gastric emptying in subjects with obesity
- Julie B. Hjerpsted, PhD,corresponding author 1 Anne Flint, PhD, 1 Ashley Brooks, MBChB, 2 Mads B. Axelsen, MD, 1 Trine Kvist, PhD, 1 and John Blundell, PhD 3
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5836914


