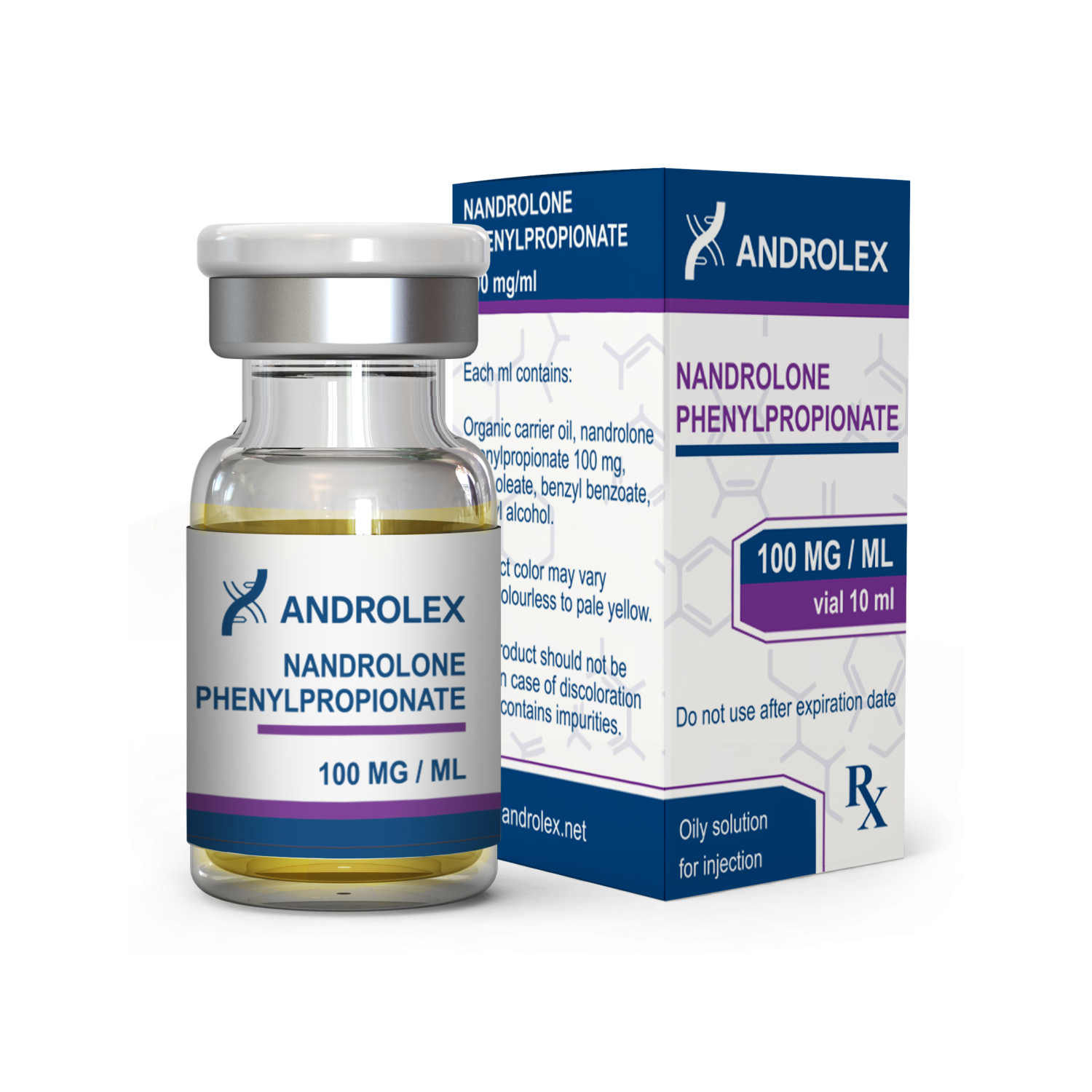




- Stock: Out Of Stock
- Package: 100 MG/ML
This offer ends in:
What is nandrolone phenylpropionate
Nandrolone phenylpropionate, often called NPP, is a short-acting form of nandrolone.
It was one of the first nandrolone esters developed and remains popular for its fast onset and clean anabolic profile.
Compared with nandrolone decanoate, NPP starts working faster and leaves the system sooner, which allows more precise control over results and side effects.
Athletes choose NPP for improved recovery, joint comfort, and steady lean muscle gain without the water retention often seen with other bulking agents.
Its short ester also makes it easier to adjust dosage and cycle duration.
Main effects of nandrolone phenylpropionate
💪 Promotes lean, dense muscle growth
🦵 Strengthens connective tissues and joints
⚖️ Improves nitrogen retention and protein synthesis
🩸 Supports red blood cell production and oxygen delivery
🔥 Speeds up post-workout recovery
💧 Provides mild lubrication effect for joints
How to take nandrolone phenylpropionate
Administration
- Route: deep intramuscular injection
- Frequency: every 2–3 days due to short half-life
- Injection sites: gluteal or thigh muscles
Dosage
- Common range: 200–400 mg per week
- Cycle length: 6–10 weeks
- Often combined with testosterone propionate or enanthate for balanced androgen support
NPP is favored by those who prefer shorter cycles or faster system clearance compared to decanoate-based compounds.
Possible side effects
- Suppression of natural testosterone
- Possible increase in prolactin levels
- Mild water retention (usually minimal)
- Oily skin or acne in sensitive users
- Temporary libido fluctuations if used alone
Contraindications
- Prostate carcinoma
- Severe liver, kidney, or heart disease
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Allergy to nandrolone or carrier oil
How to store
- Store at 20–25 °C (68–77 °F)
- Keep in a dark, dry place away from heat and light
- Do not freeze
How does nandrolone phenylpropionate work
Nandrolone phenylpropionate works by binding to androgen receptors in muscle and bone tissue.
It enhances protein synthesis, helps retain nitrogen, and stimulates the production of red blood cells, improving recovery and endurance.
Because it converts into dihydronandrolone (DHN) rather than dihydrotestosterone (DHT), it produces lower androgenic side effects while remaining strongly anabolic.
At the same time, nandrolone’s effect on collagen and joint structures often makes it a preferred compound for athletes recovering from heavy training or injuries.
Its shorter ester gives it a smoother, more responsive profile — results come faster, and users can fine-tune or stop the cycle easily if needed.


